WASTE TO ENERGY POWER PLANT
An innovative technology leading to innovative India with sustainable development of sources of energy.
As we are aware of the inscrutable fact that our wastes are collected by municipal society and are then landfilled but there are a lot of catastrophic impacts of land filling of waste materials we cannot get exact benefit from our wastes and cannot also protect emission of harmful methane gas which widely is a green house effect gas.
In order to make appropriate use of waste materials and protect our earth WASTE-TO-ENERGY-POWER PLANT should be established in each and every cities of our India and in colleges too so that we can generate electricity from our wastes and make our environment clean by controlling direct emission of methane gas to environment and thus protect lives of our upcoming generation and future creators. Energy from waste power plant is not much costly and profit is infinite to our society and environment. This power plant has basically 7 main components- 1. Bunker 2. Combustion chamber 3. Monofills 4. Boiler 5. Air pollution controller chamber 6. Turbines 7. Electricity generating Power house.
A waste-to-energy plant is a waste management facility that combusts wastes to produce electricity. This type f power plant is sometimes called a trash-to-energy, municipal waste incineration, energy recovery, or resource recovery plant. Modern waste to energy plants are very different from the trash incinerators that were commonly used until a few decades ago. Unlike modern ones, those plants usually did not remove hazardous or recyclable materials before burning. These incinerators endangered the health of the plant workers and the nearby residents, and most of them did not generate electricity. Waste to energy generation is being increasingly looked at as a potential energy diversification strategy, especially by Sweden, which has been a leader in waste to energy production over the past 20 years. The typical range of net electrical energy that can be produced is about 500 to 600 kWh per ton of waste incenerated.Thus,the incineration of about 2,200 tons per day of waste will produce about 60 MW of electrical power.
Working of waste to energy plant
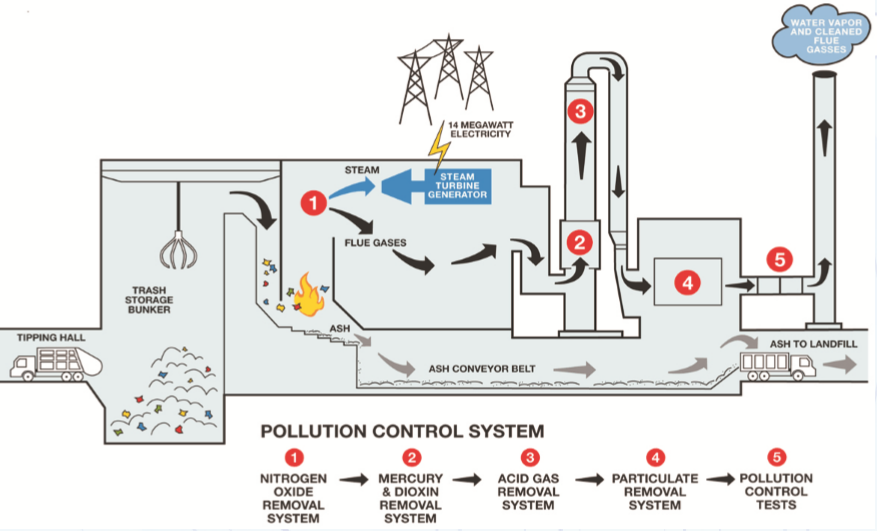 Most waste to energy plants burn municipal solid waste, but some burn industrial waste or hazardous waste. A modern, properly run waste to energy plant sorts material before burning it and can co-exist with recycling. The only items that are burned are not recyclable, by design or economically, and are not hazardous. Waste-to-energy plant are similar in their design and equipment with other steam-electric power plants, particularly biomass plants. First, the waste is brought to the facility. Then, the waste is sorted to remove recyclable and hazardous materials. The waste is then stored until it is time for burning. A few plant use Gasification, but most combust the waste directly because it is a mature, efficient technology. The waste can be added to the boiler continuously or in batches, depending on the design of the plant. In terms of volume, waste-to-energy plants incinerate 80-90 percent of waste. Sometimes, the residue ash is clean enough to be used for some purposes such as raw materials for use in manufacturing cinder blocks or for road construction. In addition, the metals that may be burned are collected from the bottom of the furnace and sold to foundries. Some waste to energy plant convert salt water to potable fresh water as a byproduct of cooling processes.
Most waste to energy plants burn municipal solid waste, but some burn industrial waste or hazardous waste. A modern, properly run waste to energy plant sorts material before burning it and can co-exist with recycling. The only items that are burned are not recyclable, by design or economically, and are not hazardous. Waste-to-energy plant are similar in their design and equipment with other steam-electric power plants, particularly biomass plants. First, the waste is brought to the facility. Then, the waste is sorted to remove recyclable and hazardous materials. The waste is then stored until it is time for burning. A few plant use Gasification, but most combust the waste directly because it is a mature, efficient technology. The waste can be added to the boiler continuously or in batches, depending on the design of the plant. In terms of volume, waste-to-energy plants incinerate 80-90 percent of waste. Sometimes, the residue ash is clean enough to be used for some purposes such as raw materials for use in manufacturing cinder blocks or for road construction. In addition, the metals that may be burned are collected from the bottom of the furnace and sold to foundries. Some waste to energy plant convert salt water to potable fresh water as a byproduct of cooling processes.
Cost of waste to energy plant
Cost of waste to energy plants may have a significant cost advantage over traditional power options, as the waste-to energy operator may receive revenue for receiving waste as an alternative to the cost of deposing waste in a landfill, typically referred to as a “tipping fee” per ton basis, versus having to pay for the cost of fuel, whereas fuel cost can account for as much as 45 percent of the cost to produce electricity in a coal-powered plant, and 75 percent or more of the cost in a natural gas-powered plant. The national solid waste management association estimates that the average united state tipping fee for 2002 was $33.70 per ton and 2190 Rs in Indian currency.
The best thing is that in this we do not need external fossil fuels to produce electricity we are just using our daily life activities waste as a source to produce electricity in this way we can save fossil fuels which are non renewable source of energy in form of electricity and finally protect our environment from harmful effects of waste materials.
Pollution control from waste-to-energy plant
Waste-to-energy plant emit less air pollution than coal plants. Waste-to-energy plants are designed to reduce the emission of air pollutants in the flue gases exhausted to the atmosphere such as nitrogen oxides, sulphur oxides and particulates, and to destroy pollutants already present in the waste, using pollution control measures such as bag houses, scrubbers, and electrostatic precipitators. High temperature , efficient combustion, and effective scrubbing and controls can significantly reduce air pollution out puts. Burning municipal waste does produce significant amounts of dioxin and furan emissions to the atmosphere as compared to the smaller amounts produce by burning coal or natural gas. Dioxins and furans are considered by many to be serious health hazards. However, advances in emission control designs and very stringent new government regulations, as well as public opposition to municipal waste incinerators, have caused large reductions in the amount of dioxins and furans produced by waste-to-energy plants. Waste to energy plant produce fly ash and bottom ash just as is the case when coal is combusted/ The total amount of ash produced by waste to energy plant ranges from 15% to 25% by weight of the original quantity of waste, and fly ash amounts to about 10% to 20% of the total ash. The fly ash, by far, constitutes more of a potential health hazard than dose the bottom ash because the fly ash contains toxic metals such as lead, cadmium, copper, and zinc as well as small amount of dioxins and furans. The bottom ash may or may not contain significant levels of health hazardous materials. In the united states, and perhaps in other countries as well, the law requires that the ash be tested for toxicity before disposal in landfills. If the ash is found to be hazardous, it can only be disposed of in landfills which are carefully designed to prevent pollutants in the ash from leaching into underground aquifers. Odor pollution can be a problem when the plant location is not isolated. Some plant store the waste in an enclosed area with a negative pressure, which prevents unpleasant odors from escaping, and the air drawn from the storage area is sent through the boiler or a filter. However, not all plants take step to reduce the odor, resulting in complaints.  An issue that affects community relationship is the increased road traffic or garbage trucks to transport municipal waste to the waste to energy facility. Due to this reason, most waste to energy plant are located in industrial areas. Landfill gas which contains about 50% methane, and 50% carbon di-oxide, is contaminated with a small amount of pollutants. Unlike at waste-to-energy plants, there are little or no pollution controls on the burning of landfill gas. The gas is usually flared or used to run or reciprocating engine or micro turbine, especially in digester gas power plants. Cleaning up the landfill gas is usually not cost effective because natural gas, which is substitute for, is relatively cheap. The plant is established in U.S. at Saugus, Massachusetts and power plant are being established in Sweden in large amount.
An issue that affects community relationship is the increased road traffic or garbage trucks to transport municipal waste to the waste to energy facility. Due to this reason, most waste to energy plant are located in industrial areas. Landfill gas which contains about 50% methane, and 50% carbon di-oxide, is contaminated with a small amount of pollutants. Unlike at waste-to-energy plants, there are little or no pollution controls on the burning of landfill gas. The gas is usually flared or used to run or reciprocating engine or micro turbine, especially in digester gas power plants. Cleaning up the landfill gas is usually not cost effective because natural gas, which is substitute for, is relatively cheap. The plant is established in U.S. at Saugus, Massachusetts and power plant are being established in Sweden in large amount.
So now the time has come when we and our government should also alter our thinking and initiate establishing waste-to-energy plants in our cities and colleges too and protect ourselves from harmful consequences of waste materials and generate electricity from our wastes and come forward as a nourishing country with implementation of such innovative ideas and techniques.
Writer: Nidya Singh (Nikky)
B.Tech 2ND year student of computer science deptt. , Mewar University
Email id – nidyasingh@gmail.com


Plasma Gasification can convert materials, normally considered waste, into energy and valuable products. Every city produces thousands of tons of solid waste per day. For example a small town will produces 500 tons of Muni l Solid Waste per day while a larger city would produce on average over 7000 tons of MSW per day. Most of the waste that we discard from our homes and businesses every day – such as non-recyclable plastics, construction debris, used tires, household trash, and sewage – contains energy. Gasification can convert the energy in all of this waste into electric power, subs ute natural gas, chemicals, transportation fuels, and fertilizers. Plasma Gasification is Not Incineration M/s.Prajwala BioEnergy No.39/A,Ground Floor,
2nd Main Road,Banagirinagar,BSK-III Stage
Bangalore-560085,India Ph 91 9663959850 91 9845311850
Email: prajwalabioenergy@gmail.com
web: http://www.prajwalabioenergy.in
Plasma Gasification can convert materials, normally considered waste, into energy and valuable products. Every city produces thousands of tons of solid waste per day. For example a small town will produces 500 tons of Muni l Solid Waste per day while a larger city would produce on average over 7000 tons of MSW per day. Most of the waste that we discard from our homes and businesses every day – such as non-recyclable plastics, construction debris, used tires, household trash, and sewage – contains energy. Gasification can convert the energy in all of this waste into electric power, subs ute natural gas, chemicals, transportation fuels, and fertilizers. Plasma Gasification is Not Incineration M/s.Prajwala BioEnergy No.39/A,Ground Floor,2nd Main Road,Banagirinagar,BSK-III Stage Bangalore-560085,India Ph 91 9663959850 91 9845311850
Email: prajwalabioenergy@gmail.com
web: http://www.prajwalabioenergy.in
We are interested to know more about setting up of plant, it’s technology, setting up cost of machines & facility for large scale waste etc. Can anyone advise please. My contact details are: sks1464@gmail.com & Phone- +919029678382
Regards,
SUBHASH KUMAR